Page 14 - May2008
P. 14
May 2008 THE NATIONAL 'BuTTon BULLETIN 67
a material similar to teeth. The surface of the dried hide is usually sanded to an
evenly thin and flat surface, grinding down the denticles to reveal the underlying
pattern of white circles. After sanding, shagreen is usually dyed. Although it is
often associated with a green color, it is sometimes dyed black or vibrant colors.
When the denticles are unsanded the hide is referred to as rough shagreen. To be
precise, shark and stingray are only referred to as shagreen if denticles are visible
(ground or rough).
A sharkskin has several pattern variations as well as smooth areas, depending
on where the hide is taken fro m the body. Shark leathers can be found with
no denticle bumps appearing on the surface-while a stingray hide is covered with
denticles and is almost always ground to a flattened shagreen surface before use.
A stingray hide is different from shark only in that the natural skin is typically
lighter and it has a distinctive back ridge pattern which is often highlighted with
white paint.
• SUEDE - An interior split of the hide. It is "fuzzy" on both sides. The top grain
may also be sanded or abraded to create the fuzzy appearance.
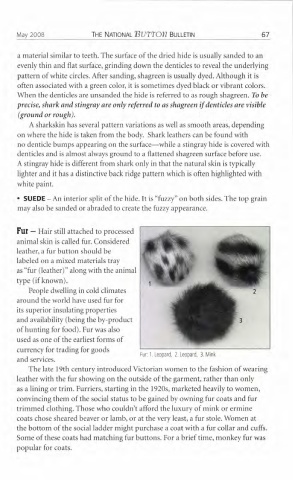
Fur - Hair still attached to processed
animal skin is called fur. Considered
leather, a fur button should be
labeled on a mixed materials tray
as "fur (leather)" along with the animal
type (if known).
People dwelling in cold climates
around the world have used fur for
its superior insulating properties
and availability (being the by-product
of hunting for food) . Fur was also
used as one of the earliest forms of
currency for trading for goods
Fur: 1. Leopard, 2. Leopard, 3. Mink
and services.
The late 19th century introduced Victorian women to the fashion of wearing
leather with the fur showing on the outside of the garment, rather than only
as a lining or trim. Furriers, starting in the 1920s, marketed heavily to women,
convincing them of the social status to be gained by owning fur coats and fur
trimmed clothing. Those who couldn't afford the luxury of mink or ermine
coats chose sheared beaver or lamb, or at the very least, a fur stole. Women at
the bottom of the social ladder might purchase a coat with a fur collar and cuffs.
Some of these coats had matching fur buttons. For a brief time, monkey fur was
popular for coats.